vEdge routers can be configured to provide DHCP server functionality to allow for host IP address assignments to be made directly from a vEdge device on a customer site. DHCP servers are configurable for the service side interface.
DHCP relay (IP helper) functionality is also supported for forwarding requests from the service side network to the IP address defined as the DHCP server in a different subnet.
Direct Internet Access (DIA)
With DIA, Internet-bound traffic or public cloud traffic from the branch is routed directly to the Internet, avoiding the latency involved in tunneling Internet-bound traffic to a central site. Benefits of using DIA include reduced bandwidth consumption, latency, and costs (thanks to offloading Internet traffic from the private WAN circuit). Employees at remote branch offices experience improved connectivity to Internet sites via DIA. IP NAT is enabled on the Internet transport interface to handle private-to-public IP address translations.
Security Design
Cisco SD-WAN offers four security categories for both integrated on-premises and cloud deployments: network segmentation, enterprise firewall, secure web gateway, and DNS-layer security. The following security features are included:
- IPsec encryption
- Intrusion prevention system
- App controls
- Malware protection
- SSL/TLS decryption
vEdge routers are also equipped with a stateful firewall to ensure that user traffic is restricted to authorized destinations and to provide auditing of security incidents.
VPN Segmentation
Segmentation via VPNs is another security feature of the Cisco SD-WAN solution. It is similar to virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) segmentation on Cisco IOS routers. Segmentation is initiated in the control plane and enforced in the data plane. Each VPN is assigned a value from 0 to 65530, where 0 and 512 are reserved for system use. Each VPN has traffic and has its own forwarding table.
VPN 0 is the transport VPN and contains the interfaces that connect to the WAN transports (MPLS and IPsec). DTLS/TLS connections to vSmart or between vSmart and vBond are initiated from VPN 0. VPN 512 is the management VPN; it carries out-of-band management traffic. This VPN is not carried across the overlay network.
Figure 11-11 shows an example in which different VPN segments are available at different sites. Some sites have VPN 1, which is carried over to only two other sites. VPN 2 is available and transported between three sites. VPN 3 is only carried by the SD-WAN overlay between two sites.
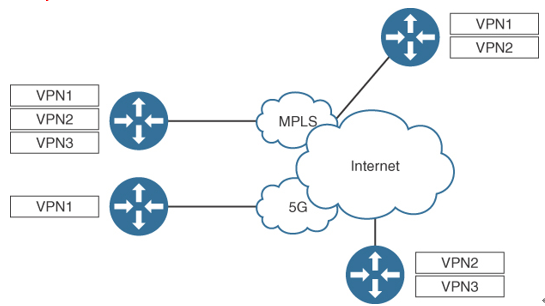
Figure 11-11 SD-WAN VPN Segmentation